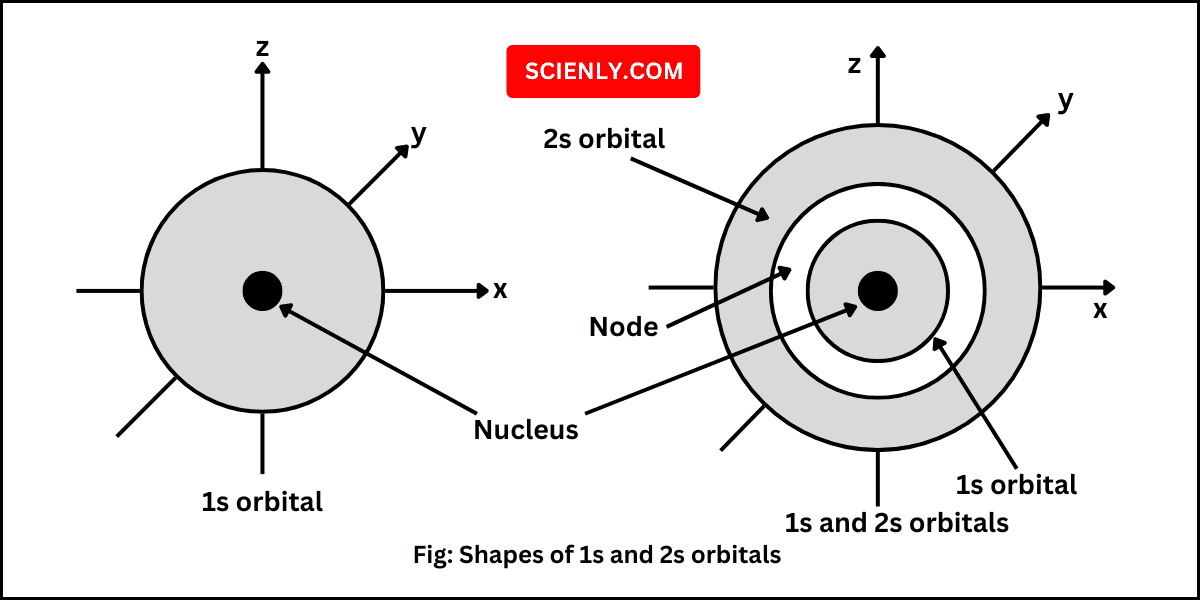
Shapes of Orbitals
In this chapter, we will learn about shapes of orbitals. We know that an atomic orbital is the three-dimensional region or area in space around the nucleus in which the tendency of finding an electron is maximum. The square of…

In this chapter, we will learn about shapes of orbitals. We know that an atomic orbital is the three-dimensional region or area in space around the nucleus in which the tendency of finding an electron is maximum. The square of…
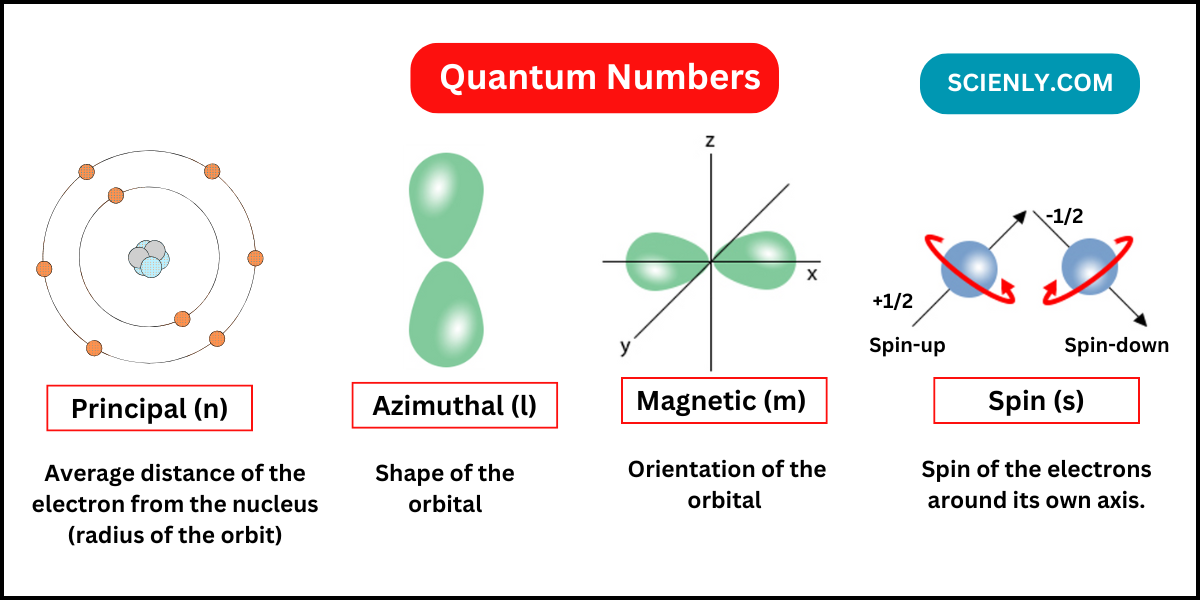
In this chapter, we will learn about quantum numbers. As you know that there are a large number of persons in the world. If you have to search a particular person in this world, at least four things are needed:…
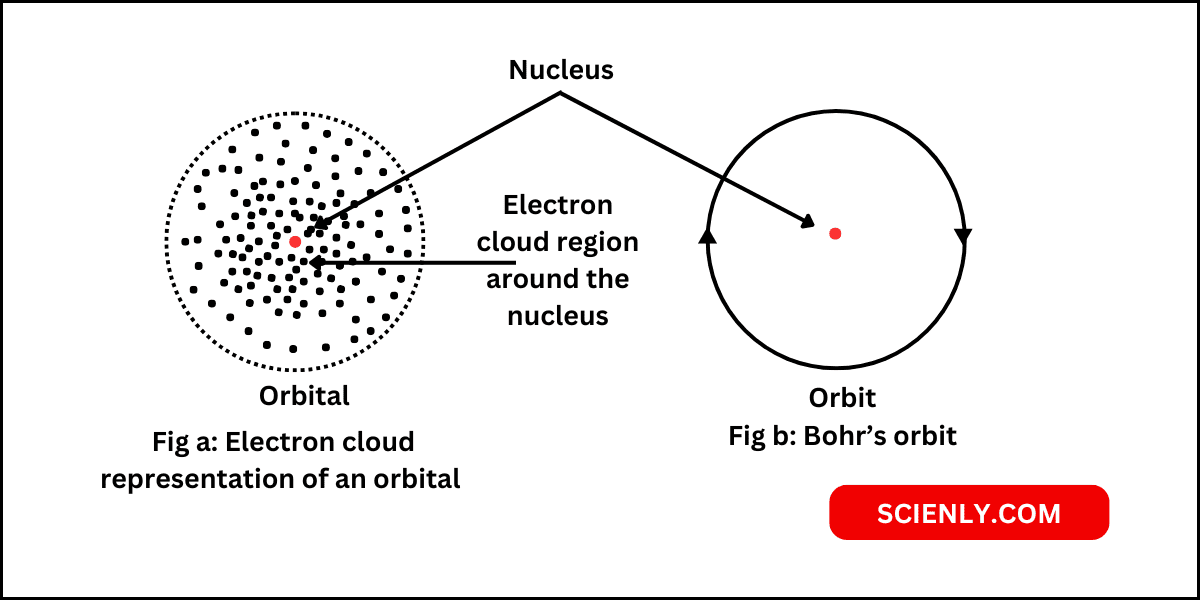
Atomic orbital is the three-dimensional region or space around the nucleus of atom, where the probability of finding an electron is maximum (90 – 95%). In other words, an atomic orbital represents the region in the space where an electron…

Quantum mechanical model of atom is the atomic model which is based on the particle and wave nature of the electron. This model is also known as wave mechanical model of atom and Erwin Schrodinger developed it in 1926. In…

In this chapter, you will learn about the Schrodinger wave equation and its derivation. A microscopic object, such as an electron exhibits both observable wavelike and particle-like characteristics. Classical mechanics, which are based on Newton’s laws of motion, cannot explain…

In this chapter, you will learn about Heisenberg uncertainty principle. Neil Bohr’s theory assumes an electron as a material particle of small mass revolving round the nucleus in circular orbits situated at a fixed distance from the nucleus with a…
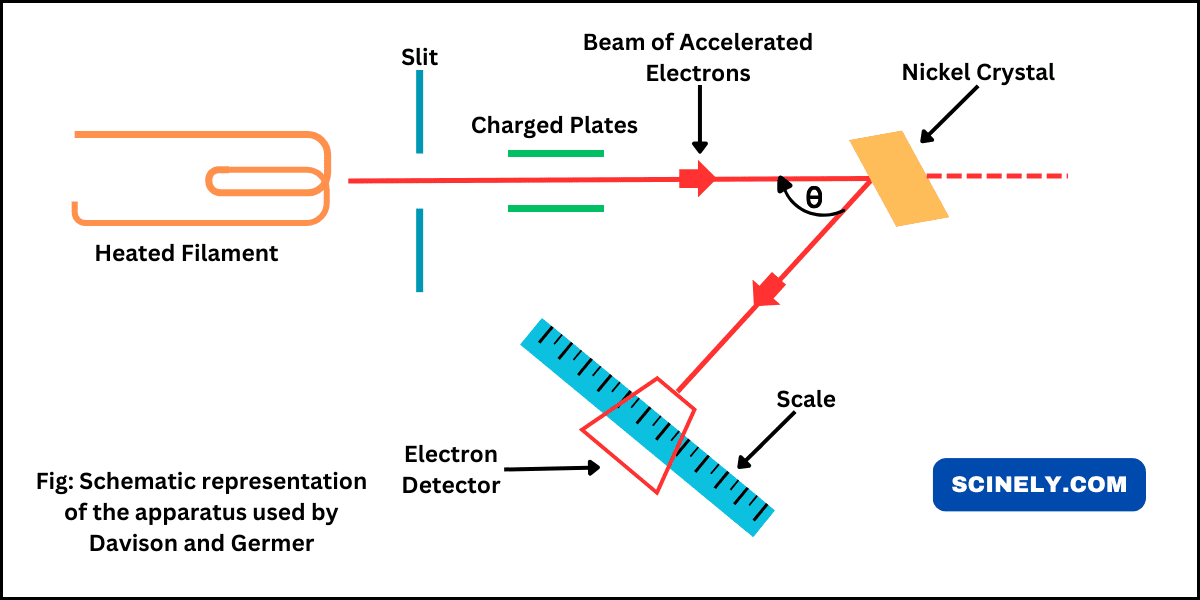
In this chapter, we will learn about the dual nature of particles: de Broglie equation or relationship. In 1905, Albert Einstein had suggested that the light has dual character, that is, sometimes it can behave as a wave as well…
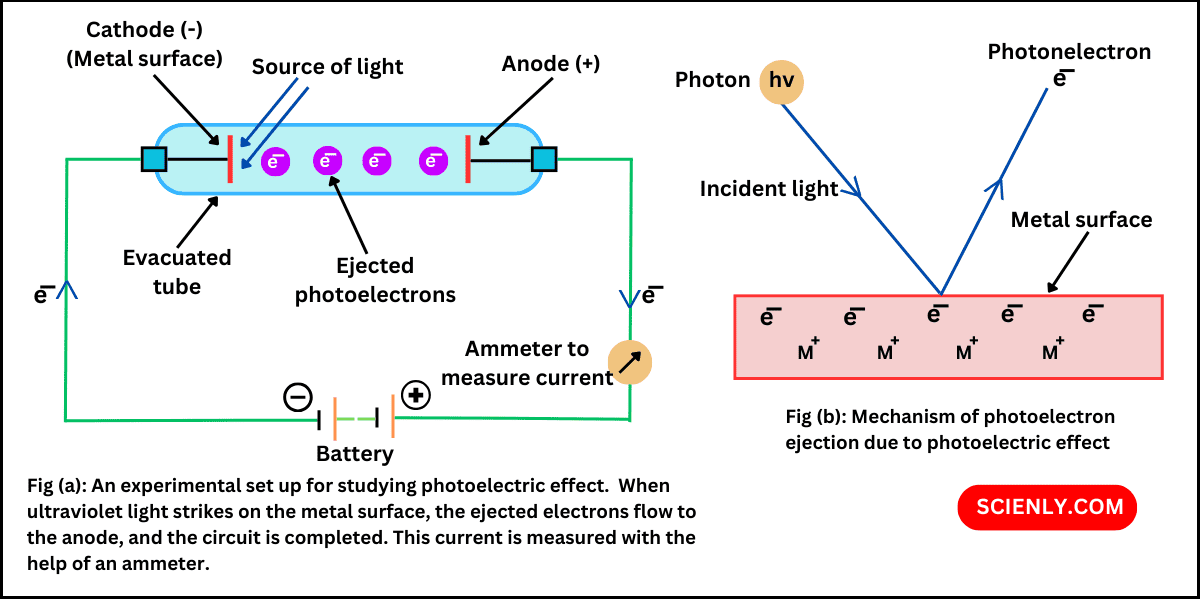
Heinrich Hertz in 1887 discovered that when a beam of light of suitable high frequency strikes on a clean metal plate (such as cesium) in vacuum, electrons are ejected (or emitted) from the surface of the metal plate. This phenomenon…
In this chapter, you will learn about the Planck’s quantum theory. Before going to learn about this theory, we will understand some few things. The wave nature of electromagnetic radiation could successfully explain some of the experimental phenomenon such as…
In this chapter, we will understand the drawbacks of Bohr’s atomic model in detail. Niels Bohr’s atomic model or theory successfully explained in a very systematic way the spectra of hydrogen atom and hydrogen like ions such as He+, Li2+,…