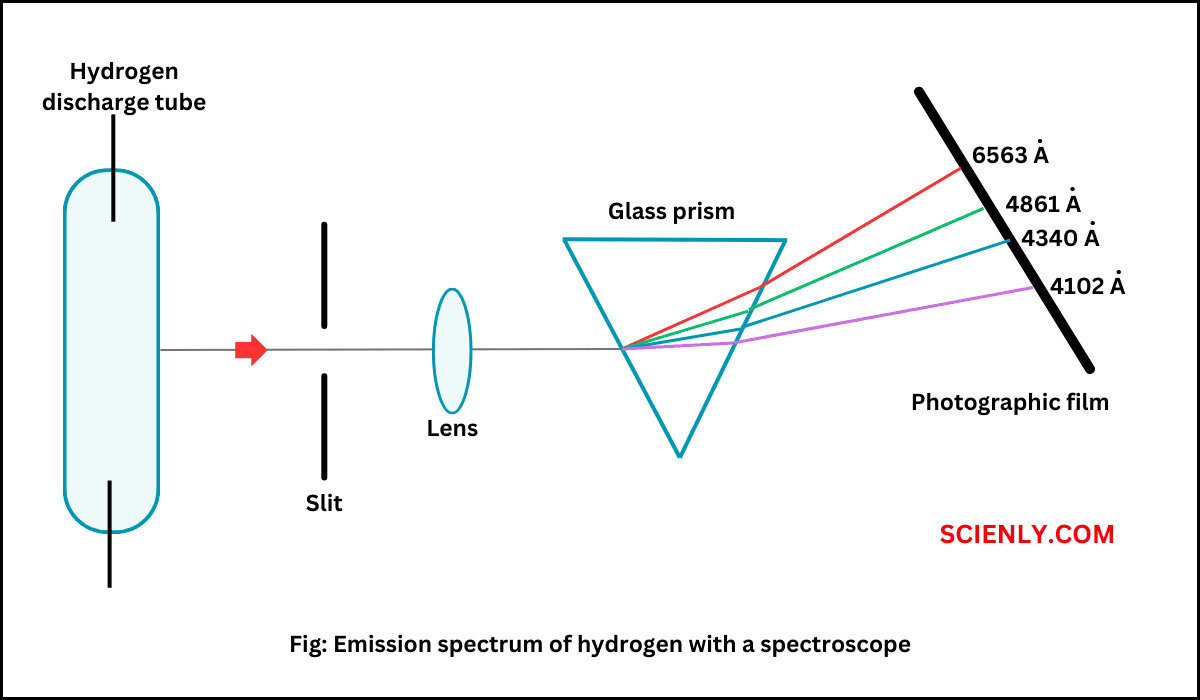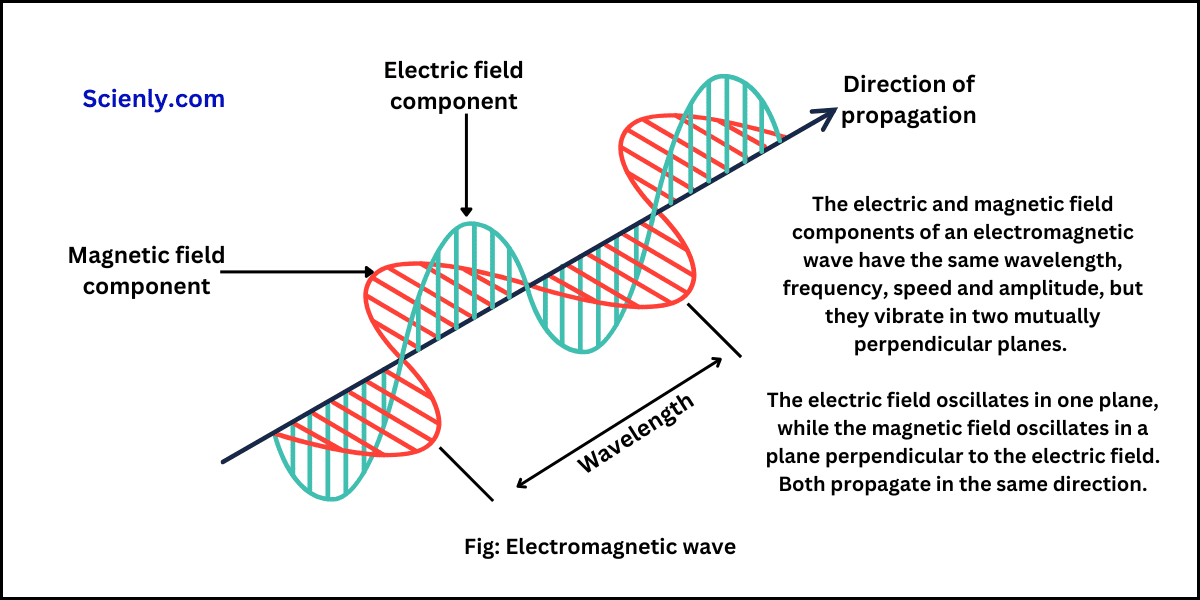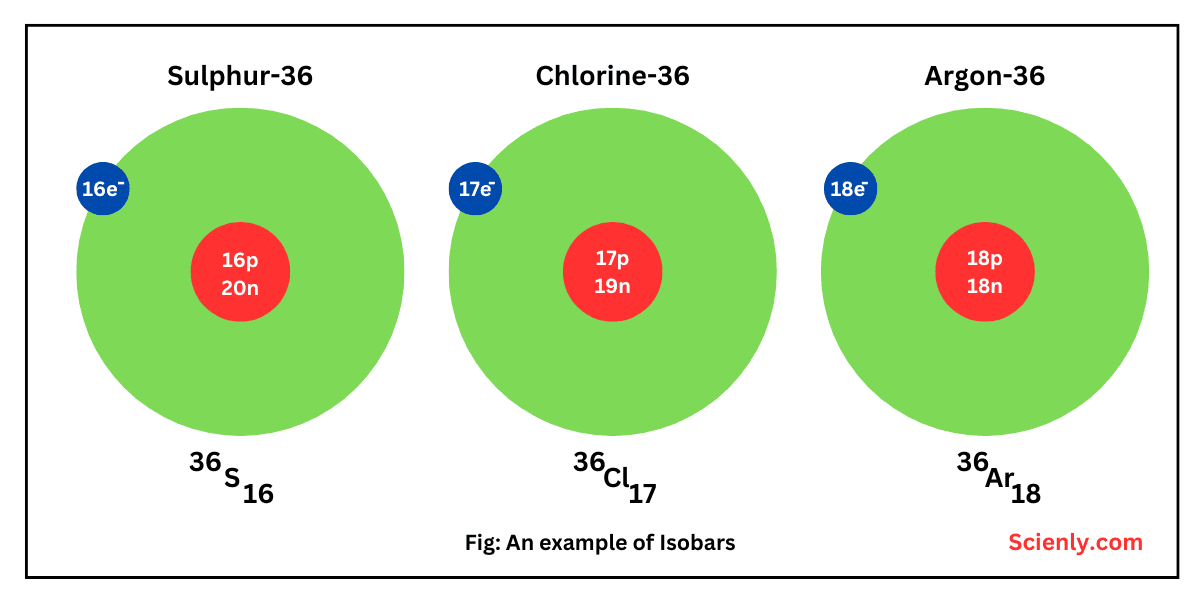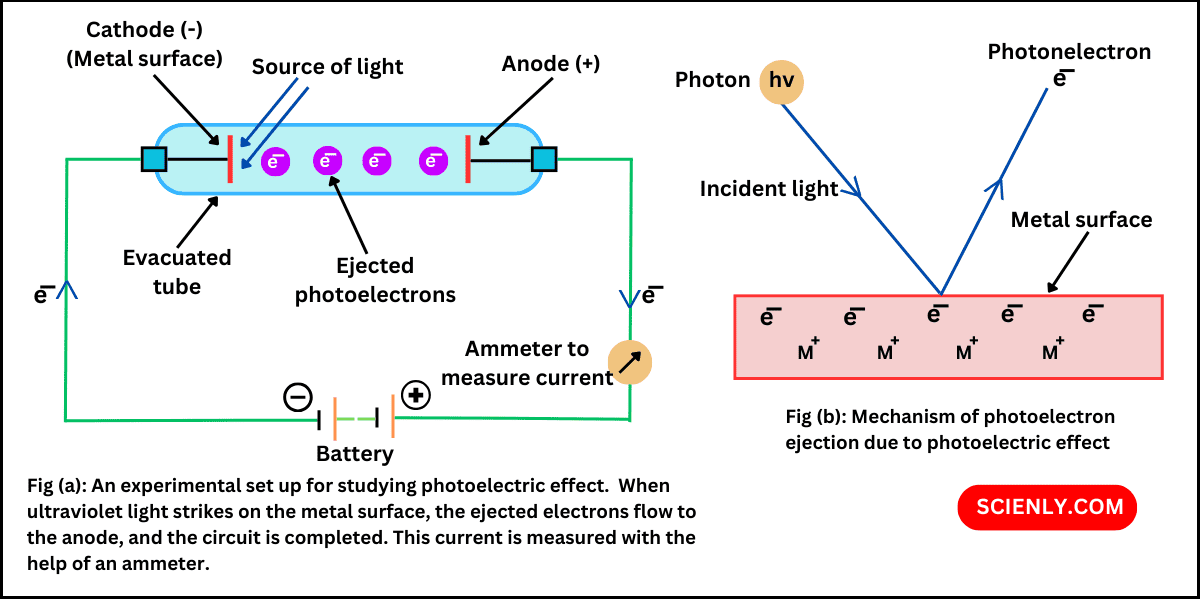
Photoelectric Effect
Heinrich Hertz in 1887 discovered that when a beam of light of suitable high frequency strikes on a clean metal plate (such as cesium) in vacuum, electrons are ejected (or emitted) from the surface of the metal plate. This phenomenon…