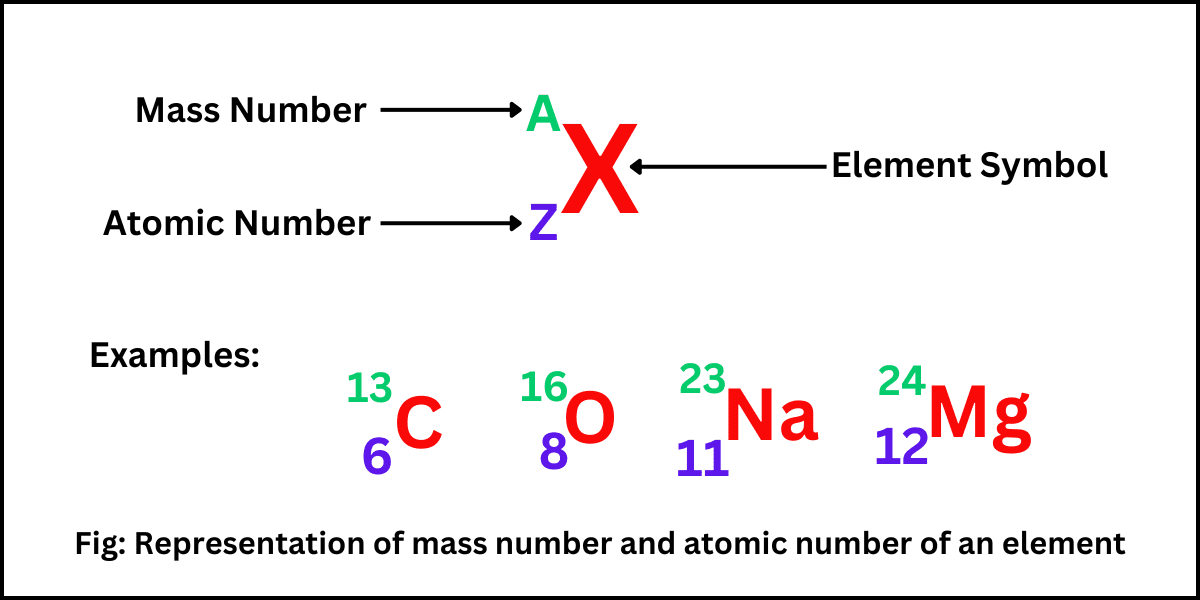
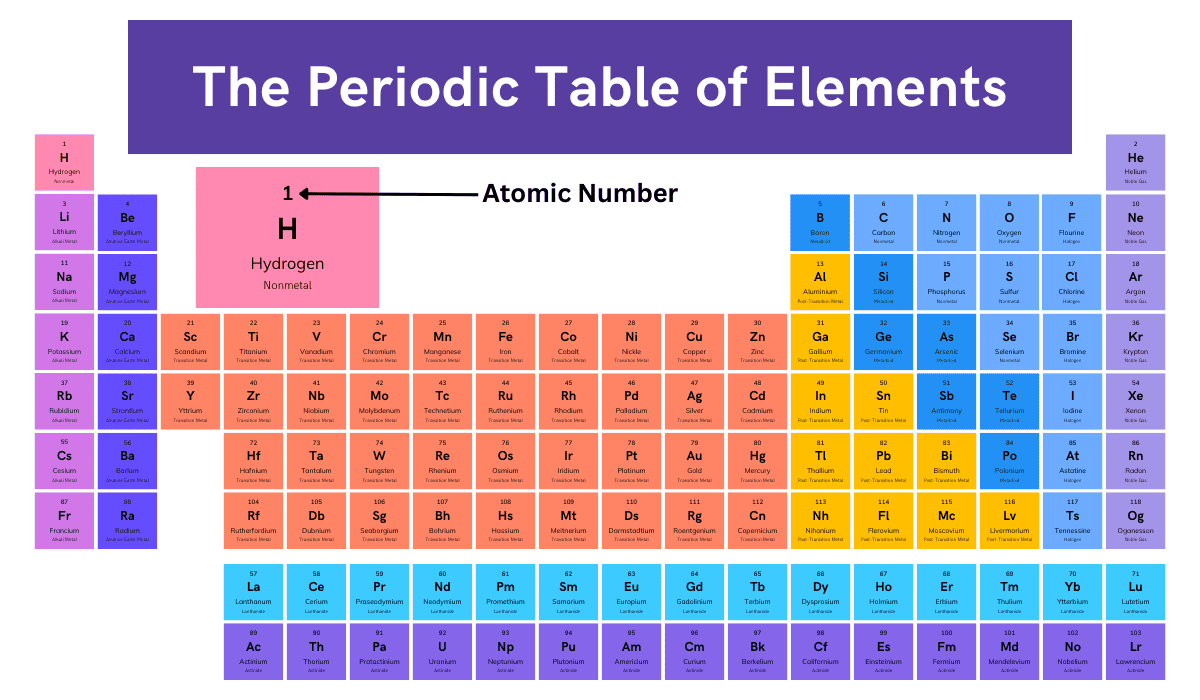
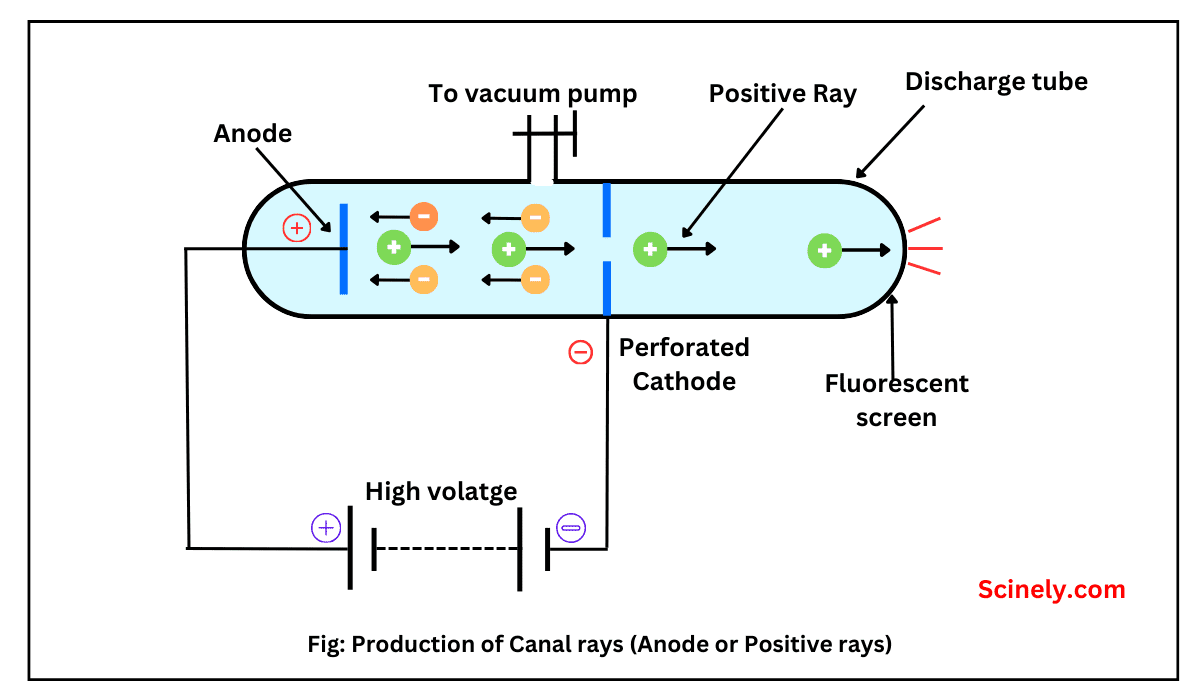
Isotopes: Definition, Meaning, Examples, Uses
All the atoms of a particular chemical element have the same number of protons in their nuclei, but the number of neutrons may be different. Such atoms have the same atomic number, but mass numbers are different because of a…